How Foundry Castings Are Shaping Industries Around the World?

You might have heard of the word casting in the production process of iron-based products. Foundry castings occupy a special position in the complex system of industrial relations. These castings are the basis for many product lines of countless pieces of equipment that are developed for several industries. But what exactly is this foundry, and why must we understand about foundry casting products? This blog will take you into the foundry environment, the steps to create castings, the materials required, the equipment used and the present trends.
What is a Foundry?
A foundry is defined as a place where metal is melted and then converted into various different shapes. These facilities are not only confined to the fabrication of metal parts; they provide a crucial part in the creation of products that are essential in our lives. Therefore, it can be said that foundry castings are a silent pillar of present-day industry, producing the components that are used to drive machinery, automobiles, and structures.
The making of these castings involves treating metal or iron in a way that forms the desired shapes, and this is achieved by pouring the metal into moulds. The metal solidifies in the mould, and when it has cooled enough, the casting is opened, and any excess material is scraped off. This process looks very simple, which, in fact, entails several sub-steps that should be perfectly implemented in order to achieve maximum efficiency.
The Casting Process: From Metal to Mold
To fully understand the foundry castings, it is necessary to take a closer look at the casting process. Some of the common stages involved in the process are pattern making, moulding, melting, pouring, ejection, cleaning, fettling and inspection.
- Patternmaking: The process starts with making what is known as a mould, which is basically a replica of what one wants to make in casting. This form is often made of wood or metal and is used to shape moulds.
- Moulding: It’s a common practice to use different types of moulds, and among them, the most commonly used material is silica sand. The contour of the mould is directly related to the casting shape to meet the final contour.
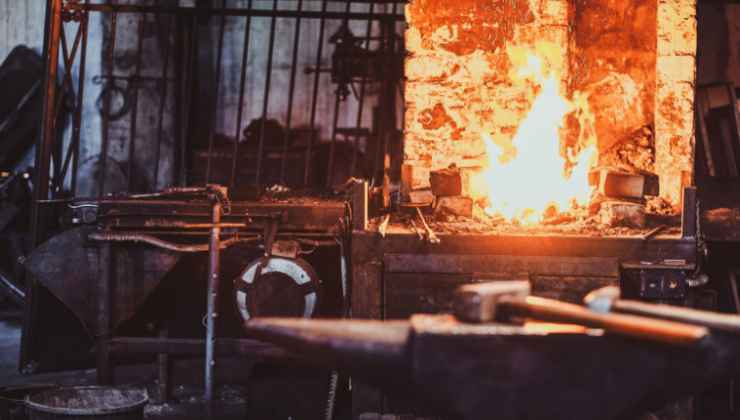
- Melting: The metal is then melted in a furnace at a specific temperature that should be constantly maintained. The molten metal is then stocked in a ladle where the impurities are removed before pouring.
- Pouring: The molten metal is then prepared and slowly poured into the mould cavity. This is an important step because any mistake made at this stage will affect the overall casting output.
- Ejection and Cleaning: After the metal has been poured and has taken the shape of the mould cavity, it then cools and solidifies, and the casting is then removed from the mould. It then undergoes washing to eliminate any type of material that might remain.
- Fettling: This process entails the removal of any excess material that may be remaining after the casting in order to get the right sizes or standards.
- Inspection: The final castings are examined closely to make sure that any flaws are visible so as to meet the quality standards of the consumers.
Every one of these steps is important when carrying out the process of producing high-quality foundry castings to meet the requirements of respective sectors.
Foundry Equipment Used For Casting Production
Today’s foundries have various machines and tools that are employed in casting production because of the complexity of the process. The tool used in foundries depends on the type of metal that is to be cast and the quantity that is to be produced.
- Furnaces: Every foundry relies heavily on the furnace, in which the metal to be formed is melted. Foundries are known to employ different kinds of furnaces, including electric arc furnaces when dealing with steel, as well as induction furnaces when dealing with non-ferrous ones such as copper. These furnaces can be relatively small for use in extraordinary work or huge installations able to melt several tons of metal.
- Molding Machines: These machines create the forms in which the molten metal is to be poured. The type of machine to be used depends on the design of the mould as well as the production requirements.
- Ladles and Cranes: After the melting of the metal, the ladling process involving the use of a ladle to pour the metal into moulds is followed. These ladles are usually big, and therefore, cranes are often used to transfer them from one place to another.
- Safety Equipment: Since working conditions in a foundry are very harsh and severely hot, greatly exposed to very dangerous conditions, safety is very crucial. Employees use specific fire-resistant clothing, head protection in the form of helmets, and face protection goggles or glasses.
Safety and Design Considerations in Foundries
Running a foundry comes with many dangers, especially when working with molten metal, which is usually at temperatures of more than 2600 degrees Fahrenheit. Some measures taken when designing foundries include protective measures for the employees to reduce the risks posed to them.
- Hazard Mitigation: The risks of operating a molten metal depend on the design of a foundry in controlling the same. Large ceilings facilitate adequate air movement, which minimises the influence of heat on workers. Flame-resistant coke and refractory materials are also used on the foundry floor to ensure that in case of an overflow of metal, there is no fire outbreak.
- Safety Procedures: There is a lot of adherence to relevant safety measures to enshrine safety processes in the operations. One of the most dangerous jobs is charging the furnace, and it has to be done with utmost care. This means that even the slightest error can lead to major disasters, pointing to the need to employ expert manpower with sufficient knowledge of the metals used in the manufacture of products.
- Worker Safety: Employees performing the work in the foundry have to wear protective clothing to protect them from heat and possible dangers at the work place. Still, these workers have the daunting task of providing for the safe and efficient production of foundry castings.
Global Excellence in Foundry Castings and Commitment to Quality
Foundries are the hidden engines of industrial manufacturing that produce the foundry castings indispensable to every industry. From the intricate selection of metals to the employed casting process, even the tools and safety measures used in a foundry are an indication of efficiency in the production of castings.
It is also important to note that other trends, such as automation and sustainable production, will define the future of the foundry business. Such operations include AKP Ferrocast for ductile and grey iron castings to different industries and supplying them to different parts of the world. Their dedication towards quality and innovation guarantees that the tradition of foundry castings will remain ideal for the growth of industries for several years to come. Contact AKP Ferrocast today and get the best quality and durable ductile and grey casting iron products for various industries. Contact us to learn how we can support your industry needs.